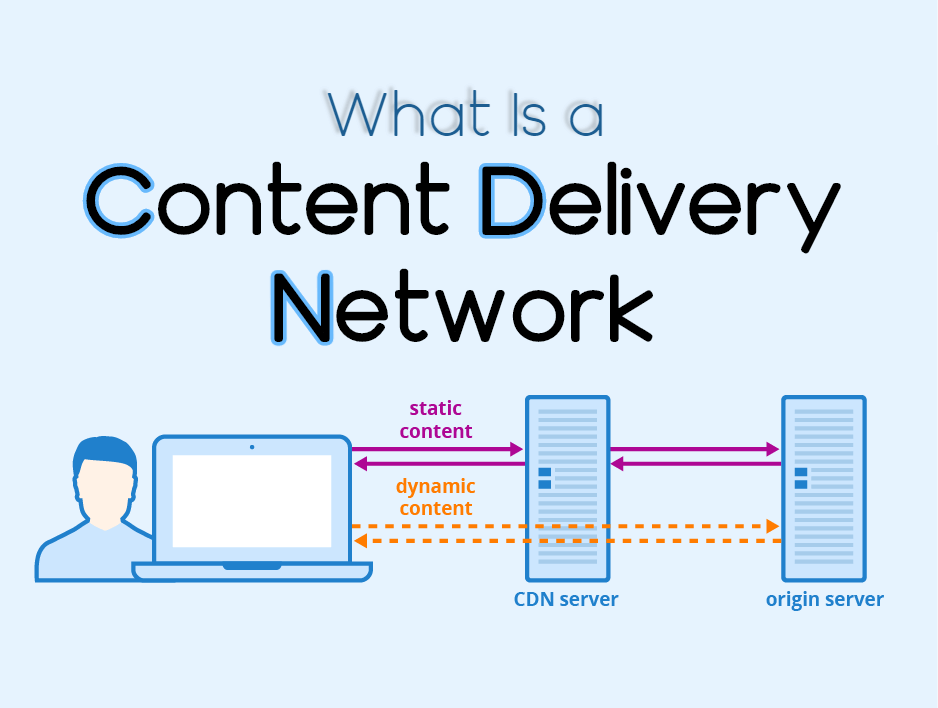
 The CDN is short for content delivery network. A content delivery network is a distributed server (network) system that provides a user with pages and other web content depending on the user’s geographic location, the origin of the site and the content delivery service.
The CDN is short for content delivery network. A content delivery network is a distributed server (network) system that provides a user with pages and other web content depending on the user’s geographic location, the origin of the site and the content delivery service.
A CDN facilitates the fast transfer of assets required for Internet content loading, including HTML pages, javascript files, stylesheets, images , and videos. It services continue to increase in popularity, and today most web traffic is served by CDNs, including traffic from major sites such as Facebook, Netflix and Amazon.
Its mission is to virtually shorten that physical distance, the goal being to improve site rendering speed and performance.
How does CDN works?
The process of bouncing through CDN is almost invisible to the user. The only way a user can know if a CDN has been accessed is if the given URL is different from the requested URL.
At its heart, a CDN is a network of servers linked to the goal of delivering content as easily, cost-effectively, efficiently and safely as possible. A CDN can position servers at the connection points between various networks in order to increase speed and reliability.
Internet exchange points (IXPs) are the primary locations where various Internet providers link to each other in order to allow each other access to traffic that originates on their different networks. By connecting to these high speed and highly interconnected locations, a CDN provider can reduce costs and transit times when providing high speed data.
Also, it allows a variety of improvements on normal client / server data transfers. CDNs place data centers at strategic locations around the globe, enhance security and are designed to survive different types of failures and congestion on the Internet.
Who uses a CDN?
It is pretty much used by anyone. In fact, it already cover over half of all traffic. With each each year, those numbers are steadily trending upward. The reality is that if any part of your business is online, there are few reasons why you should not use a CDN particularly when so many are offering their services free.
Currently, CDNs already cover over half of all traffic. With each year, those numbers are steadily trending upward. The reality is that there a few reasons why you should not use CDN although there are many that are offering their services free. Yet, even if it is free, it is not made for everyone. Especially when you are running a strictly localized website with a vast majority of your users residing in the same area as your hosting, having a CDN does not have much benefit. In fact, using a CDN can actually worsen the performance of your website by implementing another unnecessary point of connection between the visitor and an already nearby server.
Still, it is a popular choice in the following sectors:
- Advertising
- Mobile
- Media and entertainment
- Online gaming
- Healthcare
- Higher education
- E-commerce
- Government
How does a CDN improve website load times?
If a website takes a long time loading, users will reduce quickly. This is where CDN services can help to reduce load times in the following ways:
- Rather than having to connect to wherever the origin server of a website may be living, a CDN allows users to connect to a data center that is geographically closer. Less travel time means quicker service.
- Optimization of hardware and software such as powerful load balancing and solid-state hard drives can help the user get to the data faster.
- It reduce the amount of data transmitted by reducing file sizes using techniques like minification and file compression. This is because smaller file sizes mean quicker load times.
- It can also speed up sites that use TLS / SSL certificates by optimizing reuse of the link and allowing false start of TLS.
How does a CDN protect data?
Information security is an essential part of a CDN. It can secure a site with TLS/SSL certificates ensuring a high standard of authentication, encryption and integrity.
Keeping a Website Online with CDN
CDN has several functionalities that can lessen downtime:
- Load balancing distributes network traffic equally across several servers, making it easier to scale rapid boosts in traffic.
- Intelligent failover provides uninterrupted service even when one or more of the CDN servers go offline due to hardware malfunction; the failover will redistribute the traffic to the other operational servers.