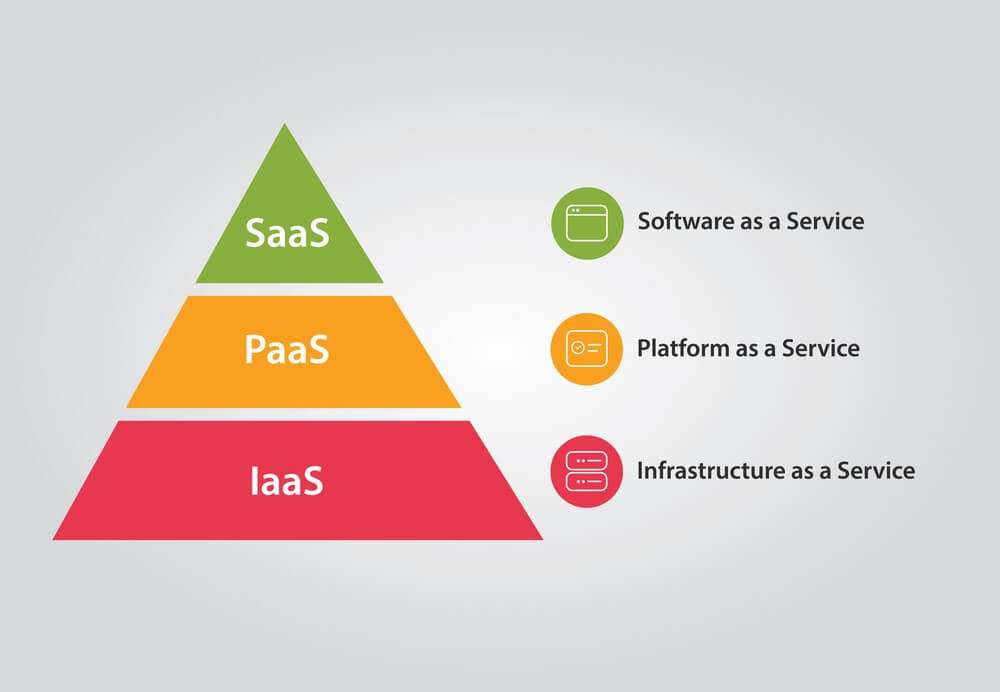
| Software as a Service | Infrastructure as a Service | Platform as a Service |
These are the three main types of cloud computing.
What is SaaS?
Software as a service, also known as cloud application services, is the most frequently used alternative on the cloud market for companies. SaaS uses the Internet to deliver applications to its users which are managed by a third-party vendor. A majority of SaaS applications run directly through your web browser, meaning that no downloads or installations are necessary on the client side. In conclusion, t is a ready software that requires no downloads or installation.
SaaS Delivery
SaaS is use over the internet. Thus, IT staff do not need to download and install applications on every computer. With SaaS, vendor handle all possible technological issues, such as data, middleware, servers, and storage resulting in smooth maintenance and business support.
SaaS Advantages
- Cost reduction. The vendors are responsible for handling the potential technical issues. Furthermore, they provide the maintenance, compliance, and security services to their users. Therefore, your expenses will be cut drastically.
- Time saving. You will not have to download and install the software on devices. As a result, the technical free does not have to worry about keeping the software on every computer up-to-date.
- Acessibility. It is accessible from any device at any time As long as you have a stable Internet connection.
- Off-the-shelf solutions. SaaS offers out-of-the-box products that are easy to set up and use. Basic packages and complex solutions are available for everyone.
Drawbacks of the SaaS model
- Lack of integration support. Many organizations need deep integration with software, data, and services on-premise. In this respect, the SaaS provider can provide limited support requiring organizations to invest internal resources in the design and management of integrations. The complexity of integrations can also restrict how to use the SaaS software or other related services.
- Insufficient data security. Large amounts of data need be shared to SaaS apps’ backend data centers to perform the software functionality needed. The transfer of sensitive business information to a public-cloud-based SaaS service could result in compromised security and compliance.
- Performance issues. Web-dependent applications that run on remote data centers can often display poor performance. At the same time, apps that are on your employees’ computers may perform much better. You should invest in a secure and quick Internet connection to prevent this problem. You also need application performance management tools to check the SaaS apps performance over time.
What is PaaS?
Platform as a Services provides users with a cloud environment for creating custom apps. PaaS provides developers with a framework which they can build on and use to create custom apps. The enterprise or a third-party vendor handle all servers, storage, and networking while the developers can control the application management.
PaaS Delivery
PaaS is almost similar to SaaS, except PaaS provides a platform for software creation. This platform is delivered over the internet, allowing developers the freedom to focus on developing the app without worrying about operating systems, software updates, storage or infrastructure. Moreover, PaaS helps businesses to develop and build applications that have specific software components incorporated into the PaaS. These applications is referred to as middleware, they are scalable and highly accessible as they take on some cloud characteristics.
PaaS Advantages
- Cost-effectiveness. You no longer need to build applications from scratch. So, if you have limited resources, or want to reduce your operating costs, it is a good option.
- Quick launch. Prebuilt backend infrastructure allows for rapid prototyping and growth. Therefore, you can release your application anytime. In turn the early launch increases the chance of success.
- Decrease development time. You have access to various libraries, frameworks, templates, and other tools. These tools will speed up and simplify the whole development process.
Drawbacks of PaaS model
- Runtime issues. PaaS applications may not be optimized for your chosen language and frameworks. Certain framework versions may not be available with the PaaS Service or function optimally. Therefore, customers may not be able to create custom dependencies.
- Data security. When data resides on third party, vendor-controlled cloud servers poses security risks and concerns. Your security options may have limit as customers might not be able to deliver services with specific hosting policies.
- Customization for legacy terms. If you have legacy applications or services, you can find that PaaS do not function that well. Thus, some customizations and configuration changes may be required to fix this problem.
What is IaaS?
Infrastructure as a service are made of highly scalable, automated computing tools. IaaS full self-service for accessing and monitoring networking, storage, and other services. Also, it provides users with cloud-based options, so companies can stop investing in costly on-site resources.
IaaS Delivery
IaaS delivers over the internet. It provides the same technologies and capabilities as a traditional data center without having to maintain or manage everything physically. Furthermore, IaaS clients also have direct access to their servers and storage, but all of this is outsourced in the cloud through a “virtual data center”.
IaaS Advantages
- On-demand scalability. IaaS is easily scalable, depending on the company’s growing business needs. IaaS providers have the most efficient storage and networking technologies to match their customers’ need.
- Great reliability. Internet connection failure would not affect the infrastructure. Besides, in general IaaS providers distribute the workload of the program across multiple data centers and servers.
- Operational flexibility. IaaS allows your team to access regularly used hardware, computing power and applications. Thus, this help them to access the necessary files and data any time and any where.
Drawbacks of IaaS model
- Issues with legacy systems. Legacy programs can run in the cloud. Nevertheless, the infrastructure unable to protect such apps. This fact forces you to enhance your application before moving it to the cloud.
- Internal training is a must. Your team has to know how to manage new infrastructure. Otherwise, the monitoring and resource management process can get too complicated.
- Lack of flexibility. IaaS vendors maintain the software, but they do not upgrade the software for some of the businesses.